Industry 4.0 is increasingly transforming factories from legacy systems to intelligent parts & smart machines to automated factories and later an ecosystem of interconnected factories and companies. What is Industry 4.0, and how does it allow these industries to make intelligent transitions? It is a short guide that offers valuable insights into Industry 4.0. Don’t miss reading!
Source: Pixabay
What’s A Smart Factory?
The term represents a highly digitized and connected world in which machines and equipment can improve operations by automating and self-optimizing. The advantages often apply beyond the actual manufacturing of products to functions, including preparation, logistic supply chain, and product growth. However, the central value of the intelligent factory also exists in the four walls. An intelligent plant’s layout will involve a mixture of manufacturing, knowledge, and communication systems, with convergence possibilities across the entire supply chain. That’s the reason why top industrial machines manufacturers are putting great stress on a smart approach.
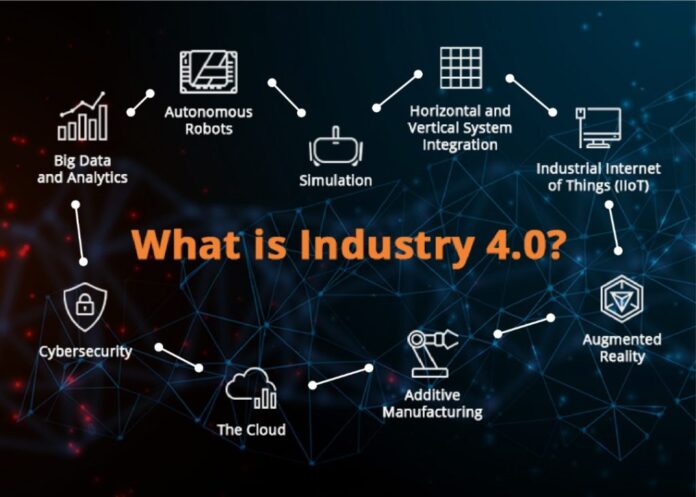
About Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is the fourth technological transformation to reform the production and manufacturing sector by incorporating digital technology developments and innovations into industrial processes. It reflects the integration of factory activities with technology advancements, including the Internet of Things, robotics, predictive analytics, cloud storage, and much more. The integration of connected machines, automation systems, and production units is enabled by industry 4.0. However, it consists of creating a physical entity using end-to-end digital transformation, internal networking, supervision workforce, automation robotics for various critical functions, sensors, pumps, actuators, PLC devices, SCADA, networking devices, cloud connectivity, IoT, and cyber protection. Adopting industry 4.0 helps manufacturers, be it Lathe Machine manufacturer or else, mitigate the production losses.
In brief, Business 4.0 incorporates some of these main aspects:
- Intelligent robots or automatic machines with limited human efforts.
- Digital Factory: intelligent equipment in factories with completely digitized functionality.
- Wired factory: several factories linked to each other through the cloud
- Smart Supply Chain: digitized inventory control, dashboards photography.
- Smart Factory Components: integrated device, smart subsystems, and wired protocols.
Source: Pixabay
Key Components
- Sensors
- Valves And Actuators
- PLC System
- Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition
- Augmented Reality / Virtual Reality
Why Become Smart? – Challenges To Traditional Companies
Understanding the challenges faced by traditional companies gives you a clear idea about the need for becoming smart in this open world.
#1. Outdated Equipment
The usage of outdated equipment and software poses challenges in certain ways, such as cost rises of output, time and manufacturing, minimal fault identification, repair needs, and preliminary data study.
#2. Study Not Easy
These end systems’ study is tough due to their complicated fault identification and maintenance process, which is typically a time-consuming activity.
#3. Retrieval of Critical Information
The retrieval of critical information from devices such as generators, pipes, motors, pumps, etc. is often a daunting aspect.
#4. Implementation
Difficulties in implementing reliable communication systems and synchronization systems that ultimately contribute to delayed processes. Problems in the detection of defects and failures are also a complicated part of this. So, Industrial machines manufacturers are transitioning to automation for enhanced business aspects.
Source: Pixabay
Benefits of Connected Factories and Industry 4.0
Multiple plants or manufacturers are operating on heterogeneous systems in a broad industry. The intelligent factory will collate these factories with intelligent devices and connect them to the cloud remotely. For connecting such fittings, LPWAN (Low Power Wide-Area Network) connectors are used, and information collected from each plant is redirected to a universal cloud connectivity gateway and user simple access for the analysis of plant working conditions. Digital factories benefit in real-time, performance monitoring, and consumer end input and output.
#1. Reduced Prices
By optimizing the usage of financial and physical properties, businesses may reduce costs during the development phase. Greater automation improves performance, whereas digital enterprise solutions may improve size and speed. This can be done by the introduction of new technology and operating platforms and by analytics.
#2. Fresh Sources of Sales
Advanced, customized goods combined with related after-sales technologies — including condition monitoring and automated business deployment — are generating new revenue streams. Companies may often use different products and services and manufacture custom-made items at the expense of bulk products.
#3. New Environment Importance
Qualitative coordination and techniques such as cooperative enterprises and cooperative go-to-market initiatives are transforming models for industry participation. Developed players have to reconsider their plans, whether through entering or forging their own established ecosystems. Ideally, better consumer service and entry to different opportunities are included.
These benefits lure the largest industrial pieces of machinery manufacturing companies to dive deep into this whole new arena of opportunities to thrive and succeed.
Source: Pixabay
Industry 4.0 – Tips To Success
Whether it be a rolling machine manufacturer or others aspiring to create a dynamic business ecosystem where smart tech plays a pivotal role, below are a few tips to help you keep going the right way.
#1. Find the Best Mix of Stability
As smart manufacturing firms are going toward stronger collaboration, knowledge exchange puts greater importance on safety. From production methods to secrets, IP properties are the crown joys of output and must be secured. Companies must balance exchanging and securing their IP properties with partners, vendors, and other third-party companies. For protection purposes, an organization’s IP may be secured by intelligent ways to exchange only parts of information while maintaining services completely functional. For instance, a business may build meta-models in place of all; it can exchange only key IP bits.
#2. Stand Out
Some producers hope to differentiate themselves from the market by quicker turnaround times, better products, and outstanding customer support. To achieve this in a digital environment, businesses need to be willing to develop and compete with other competitors who already use technology, which, therefore, lower their entry costs and raise their market pace, creating more and more diverse sources of demand. Conventional manufacturing firms must leverage emerging technology to benefit from more flexible startups’ agile and lean approaches. And it is what the world’s largest heavy equipment manufacturers need to care about.
#3. Customer Experience
The consumer today wants a smooth service with a manufacturer. When a consumer tries to order, modify a product, or discover after-sales services to increase a product’s functionality, the customer tries the same experience or a comparable experience regardless of whatever aspect of the business is being managed. The whole development life cycle – from initial distribution to after-sales facilities – must be handled on an orchestrated and structured basis to maintain this continuity and operation. Instead of different and distinct structures for manufacturing, engineering, etc., corporate processes and systems serving an organization have to be streamlined and completely incorporated. It’s a decisive part of the success of hammer machine manufacturers to manufacturers of other machines. Read More : shop.oem-automation.com
Summing Up
Considering the above discourse on Industry 4.0, any industrial paradigm now needs to embrace emerging innovations and move its legacy products to smart devices. Infochips supports several vertical businesses in Smart transformations and creates analytical and technological applications for sectors such as factory automation, power generation equipment, and actuation systems.